Research Areas
Nature-inspired Water Management & Desalination
Desalination & Water management
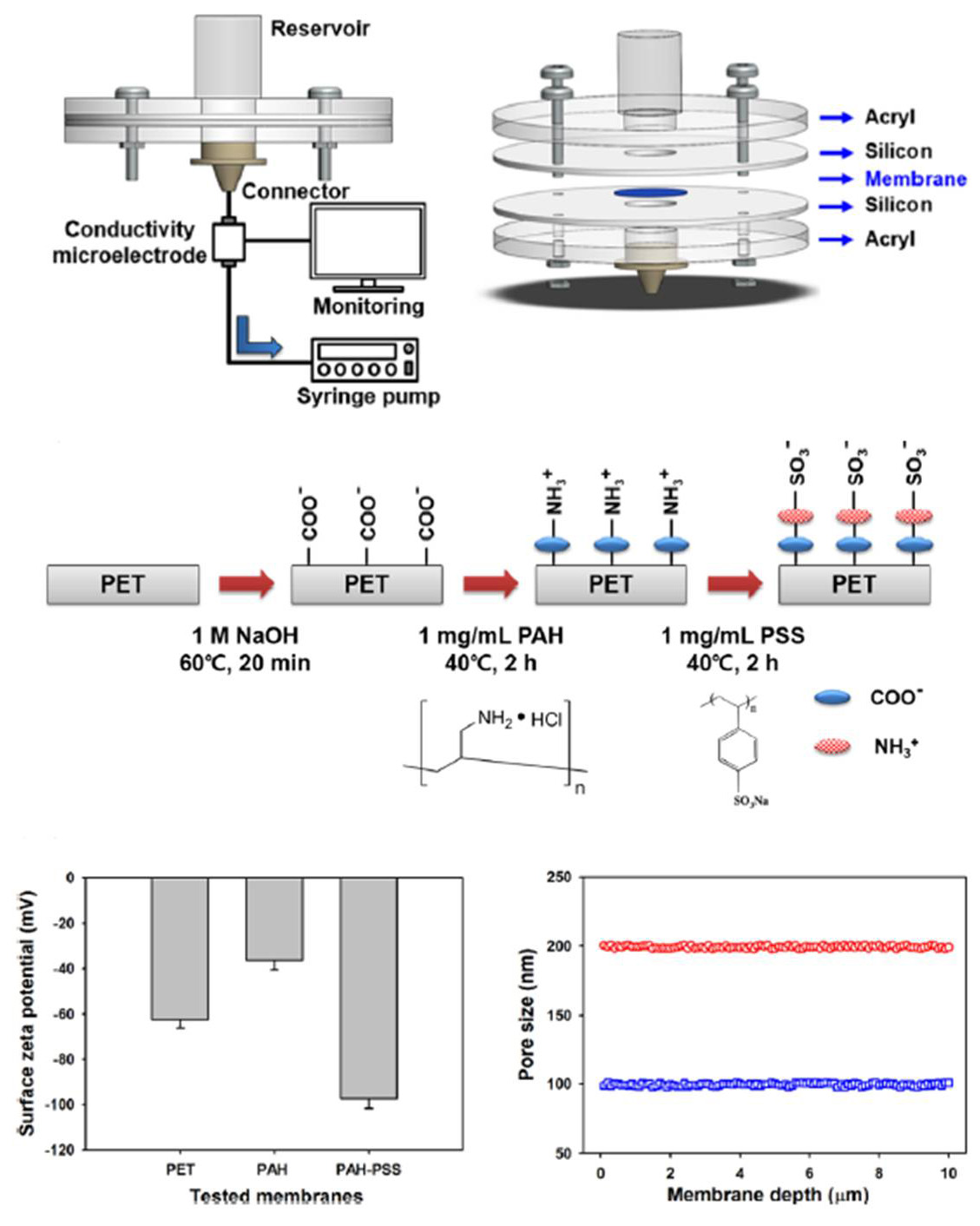
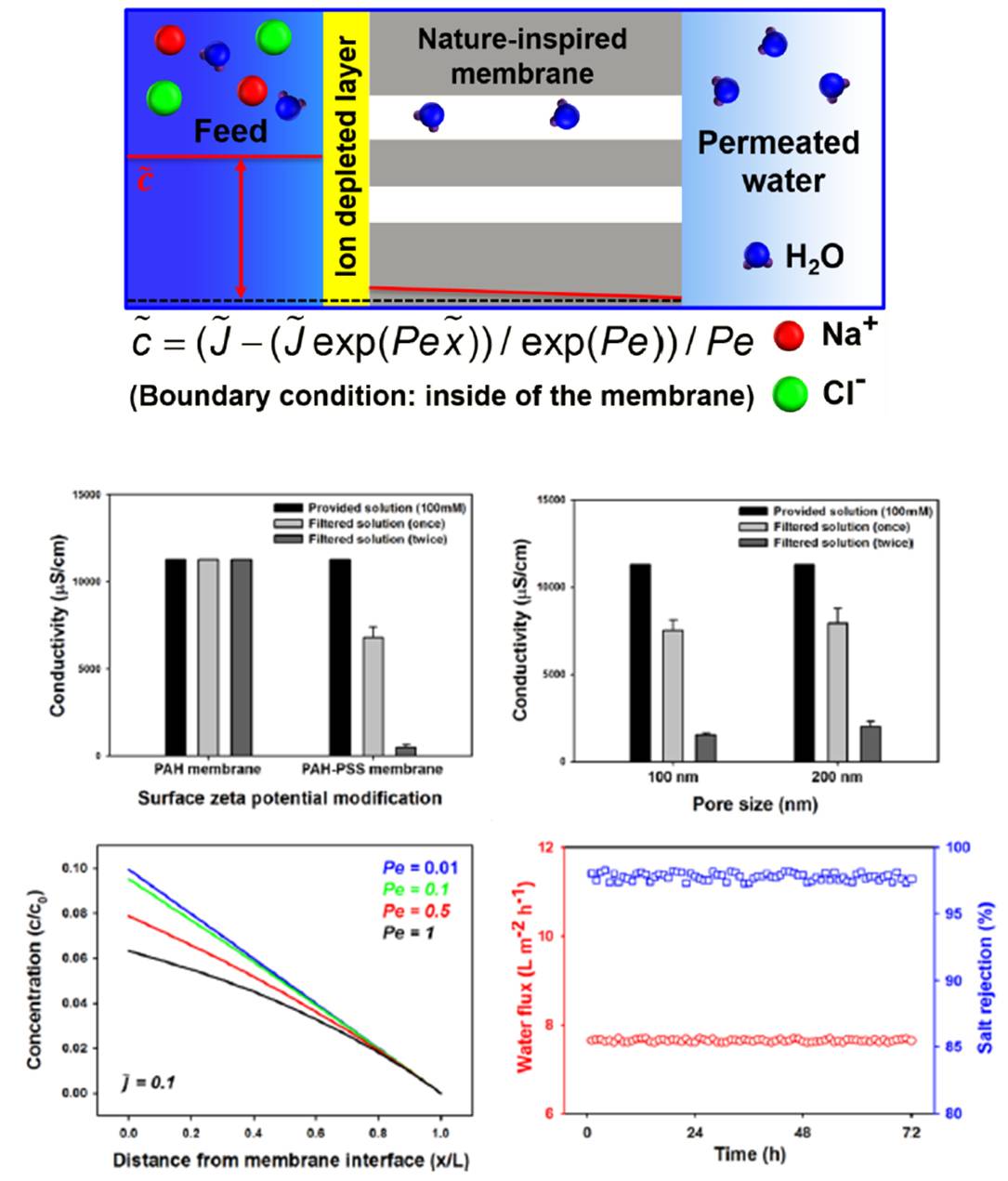
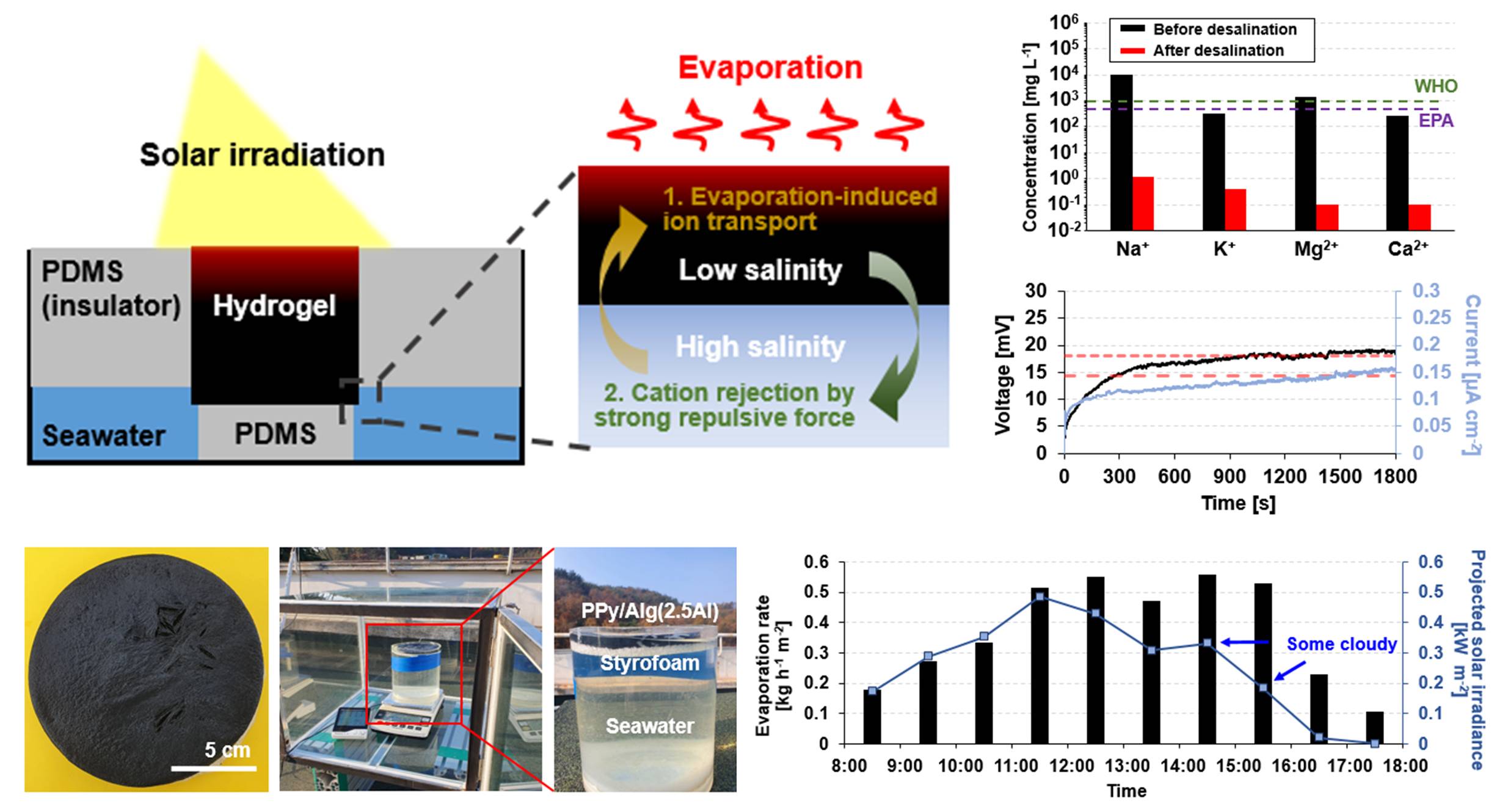
Nature-inspired seawater desalination
Salt rejection of mangrove root
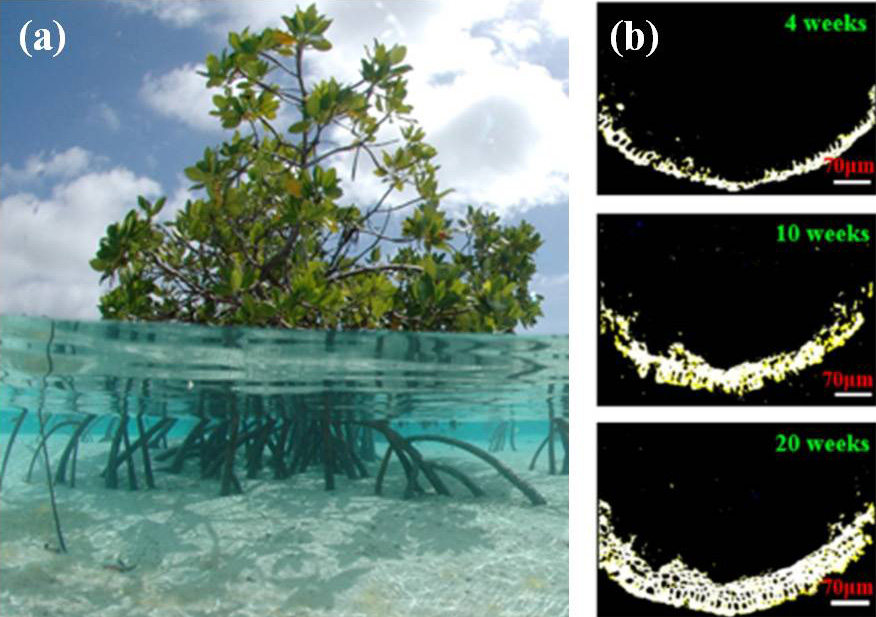
- Mangroves are adapted to salt-stress in harsh coastal condition
- Visualization of salt rejection at mangrove roots during 20 weeks
High salinity induces severe osmotic pressure difference across the cell membrane. However, mangrove species can survive in such harsh conditions. The roots of mangrove play an important role for rejecting salts without fouling.
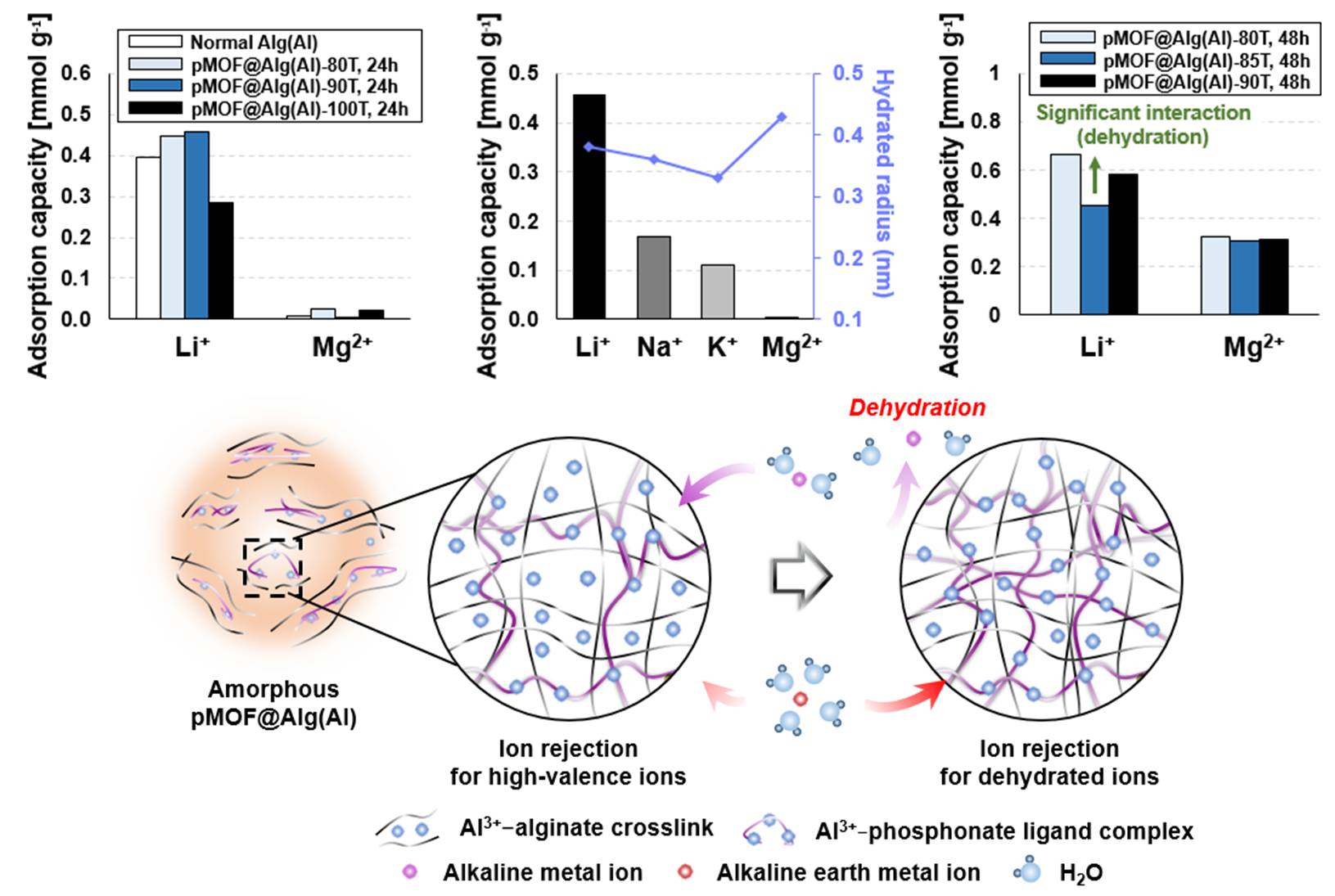
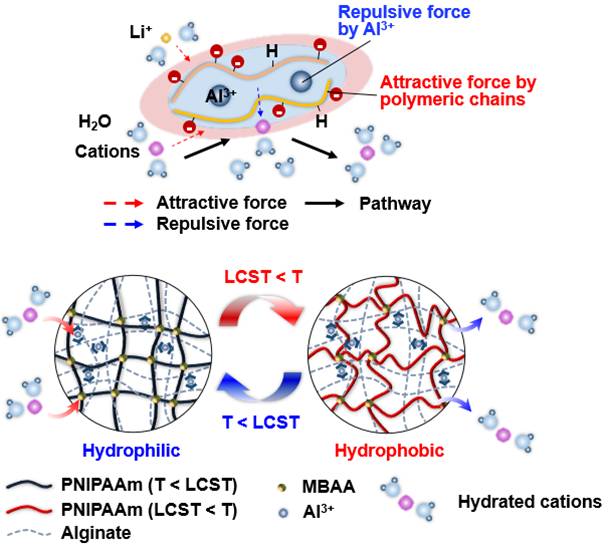
Brown algae-inspired recovery of lithium
Lithium adsorption of brown algae

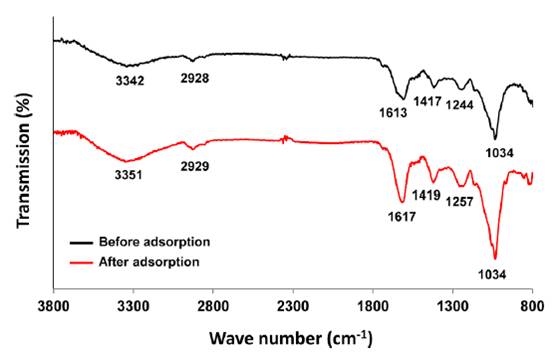
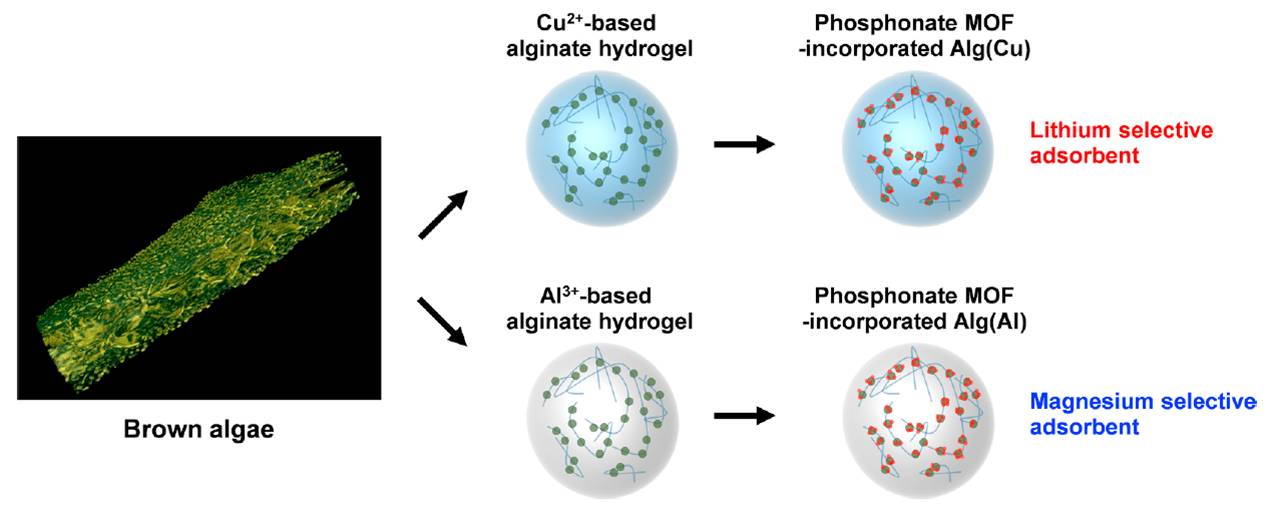
Brown algae-inspired lithium recovery technologies
Solar-based water evaporation desalination and energy generation
Solar evaporation-based energy harvesting
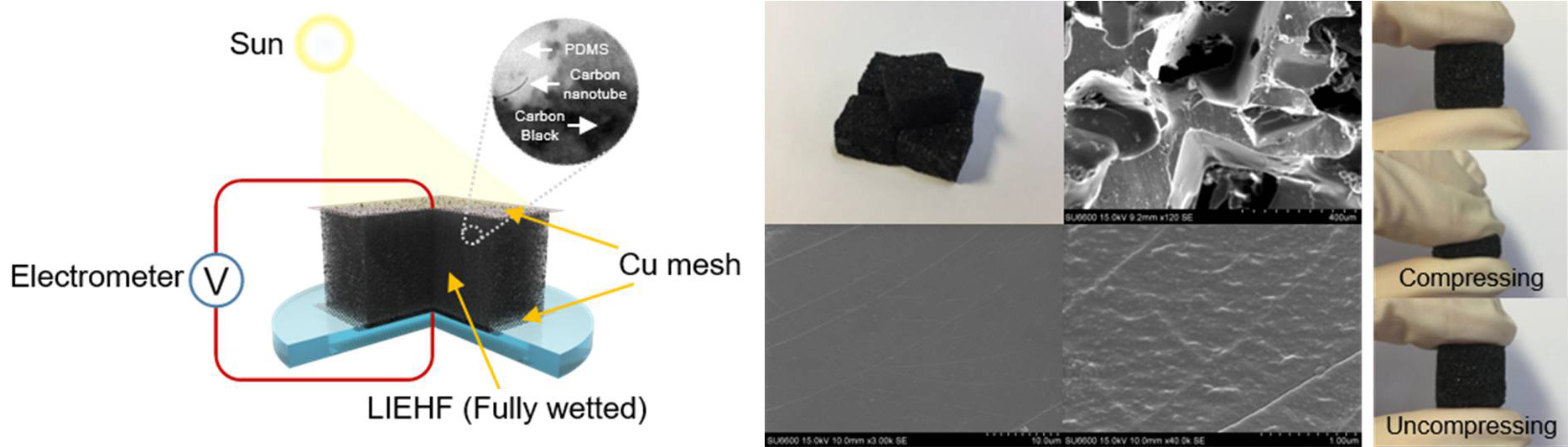
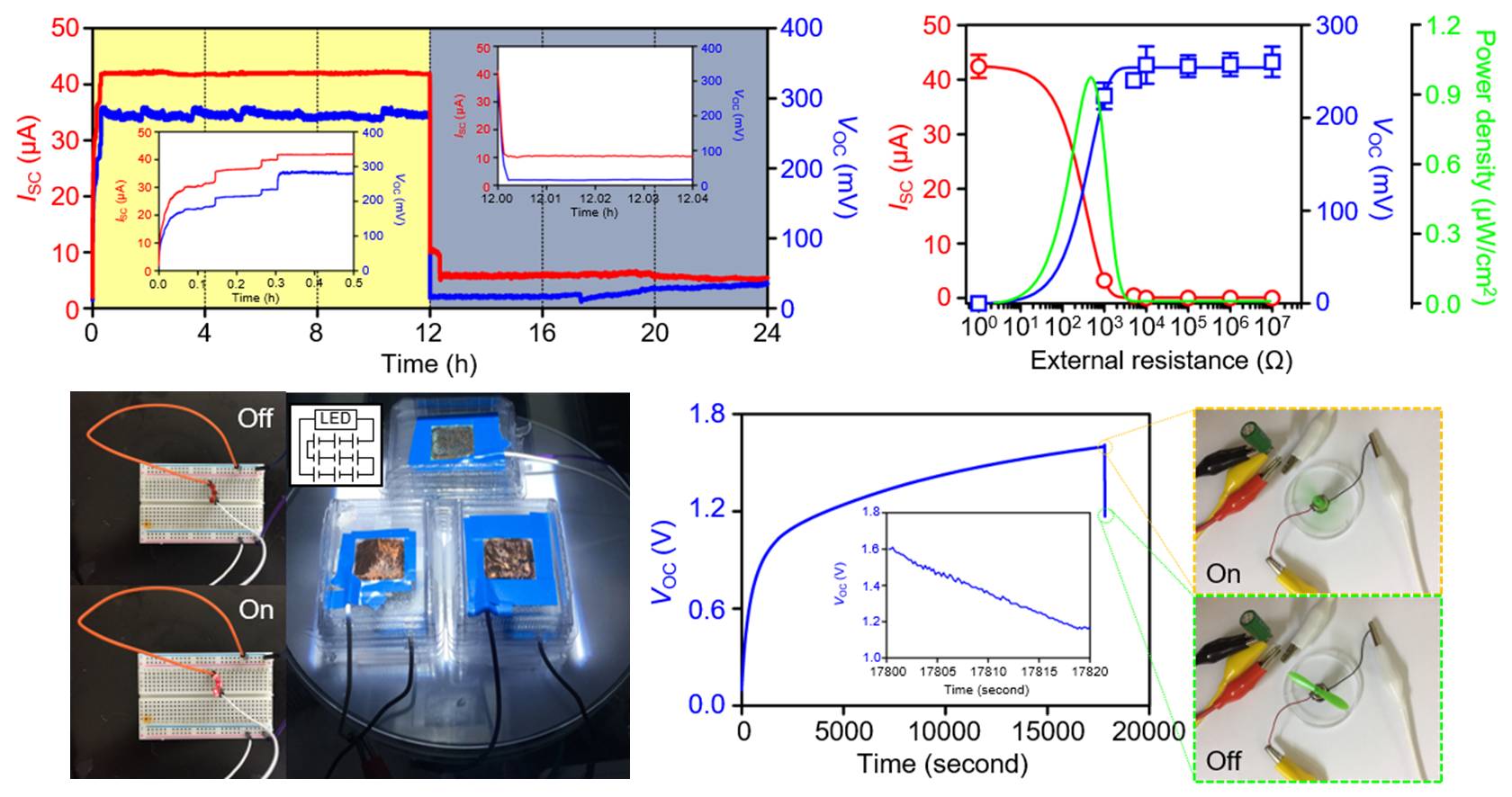
Solar evaporation-based simultaneous fresh water and electricity generation
Plant Hydrodynamics and Biomimetics
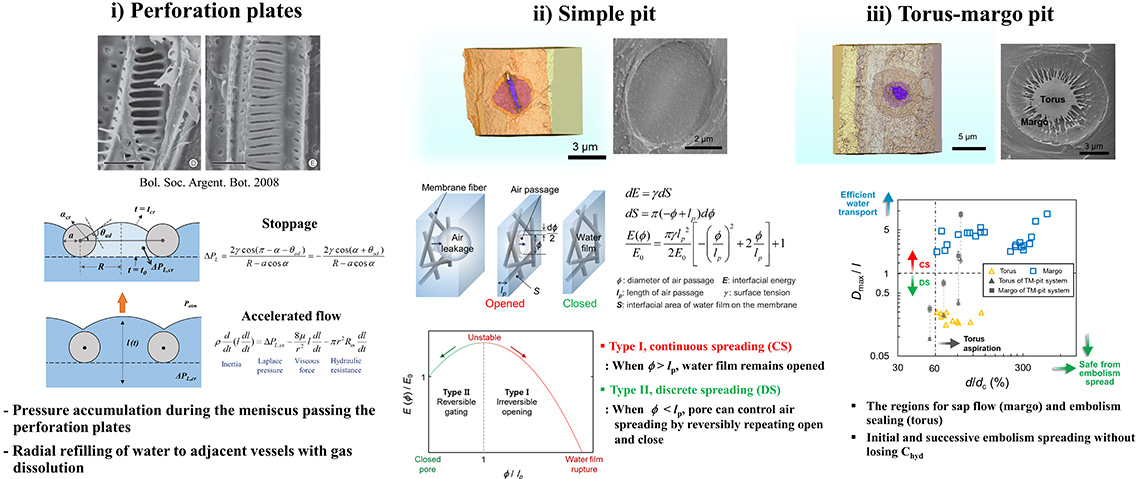
Survival strategies of plants against cavitation in xylem vessels
Bubble formation due to water transport with negative pressure
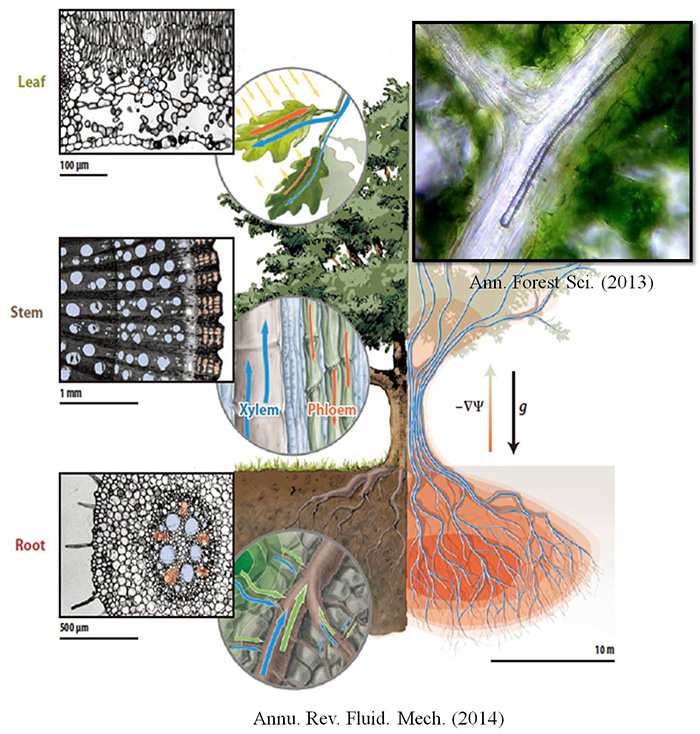
Hydrodynamic mechanisms of structural strategies of vascular plants
Water harvesting of plants under extreme environments and biomimetic devices
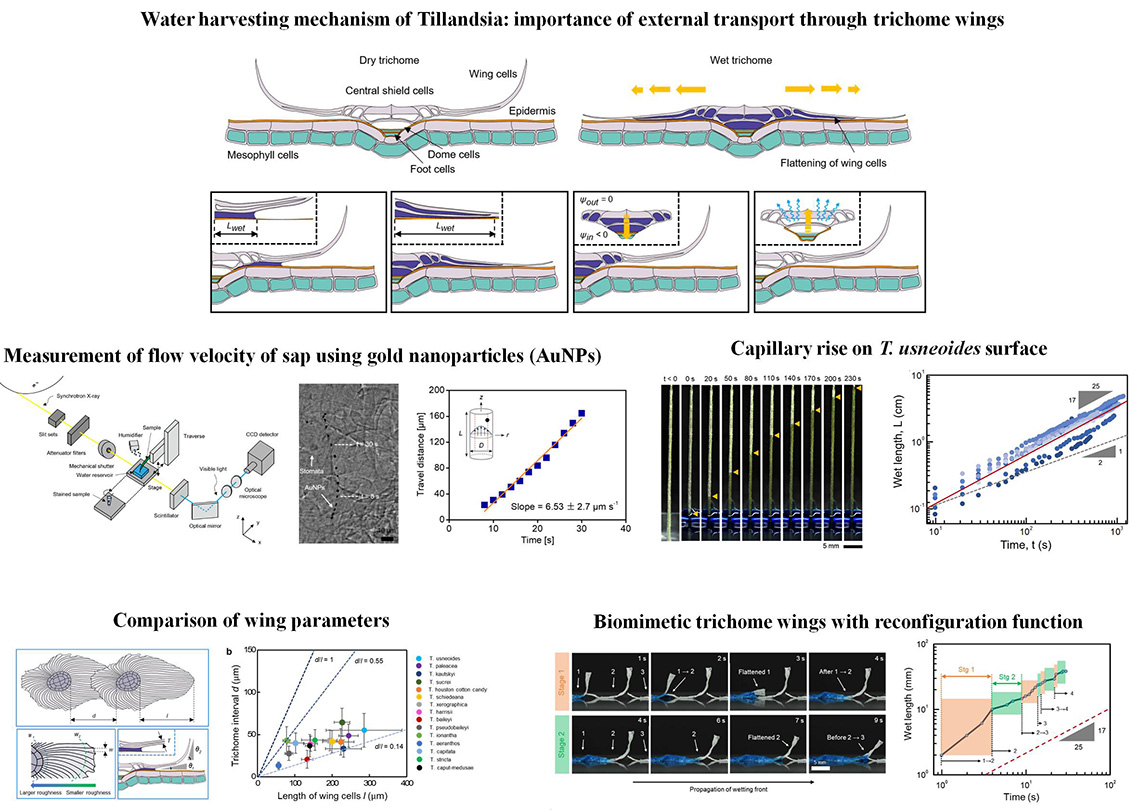
How Tillandsia usneoides transports water efficiently ?
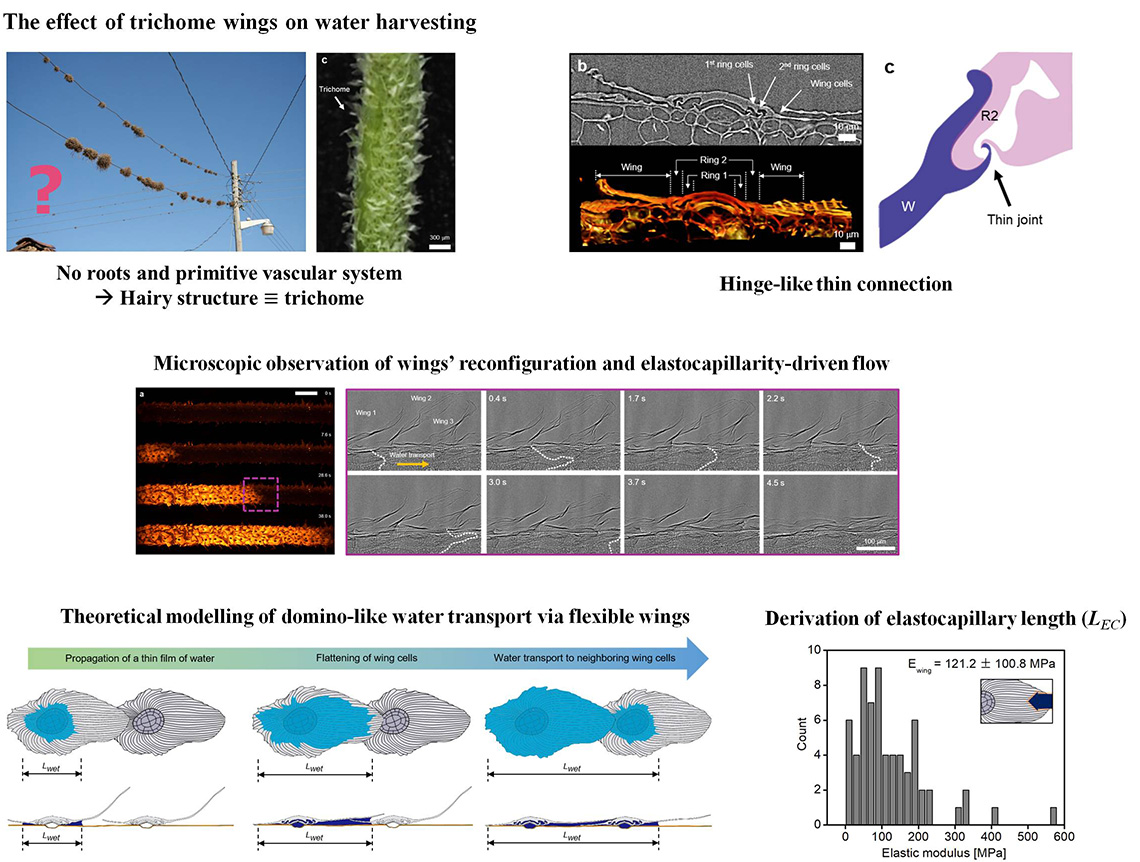
Domino-like water transport on Tillandsia via flexible trichome wings
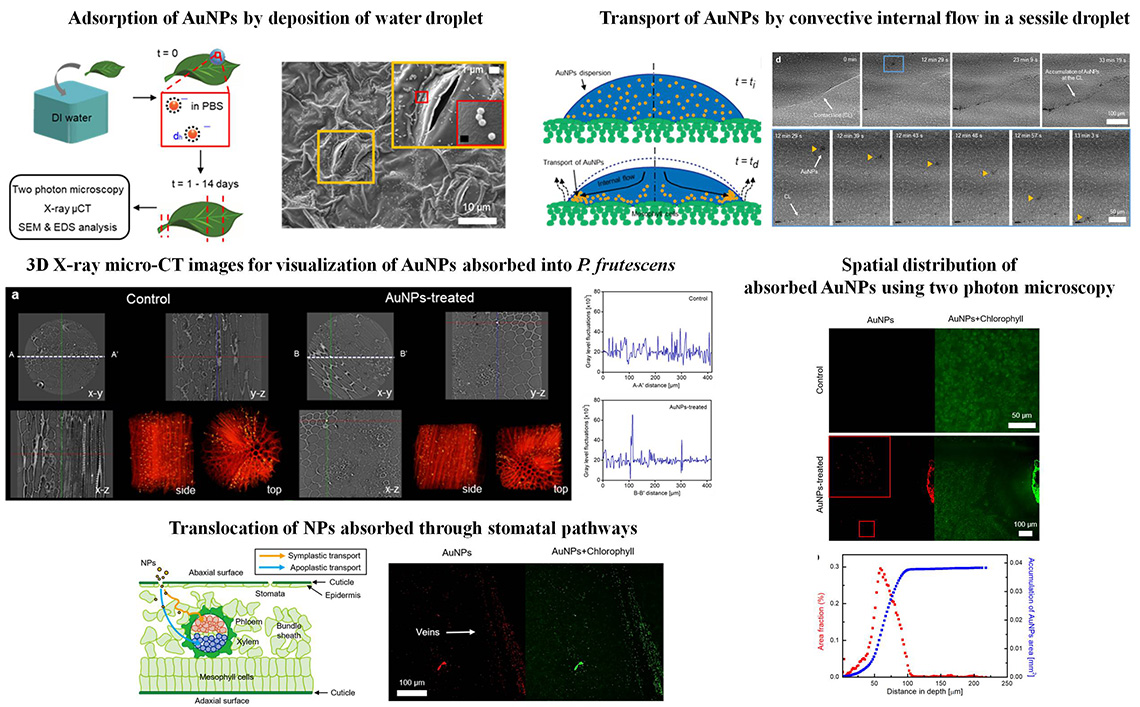
Foliar uptake of PM particles through stomatal apertures
Foliar uptake of AuNPs through stomatal apertures of Perilla frutescens
Uptake of fluorescence Q.dot in plant (garlic chive) leaves
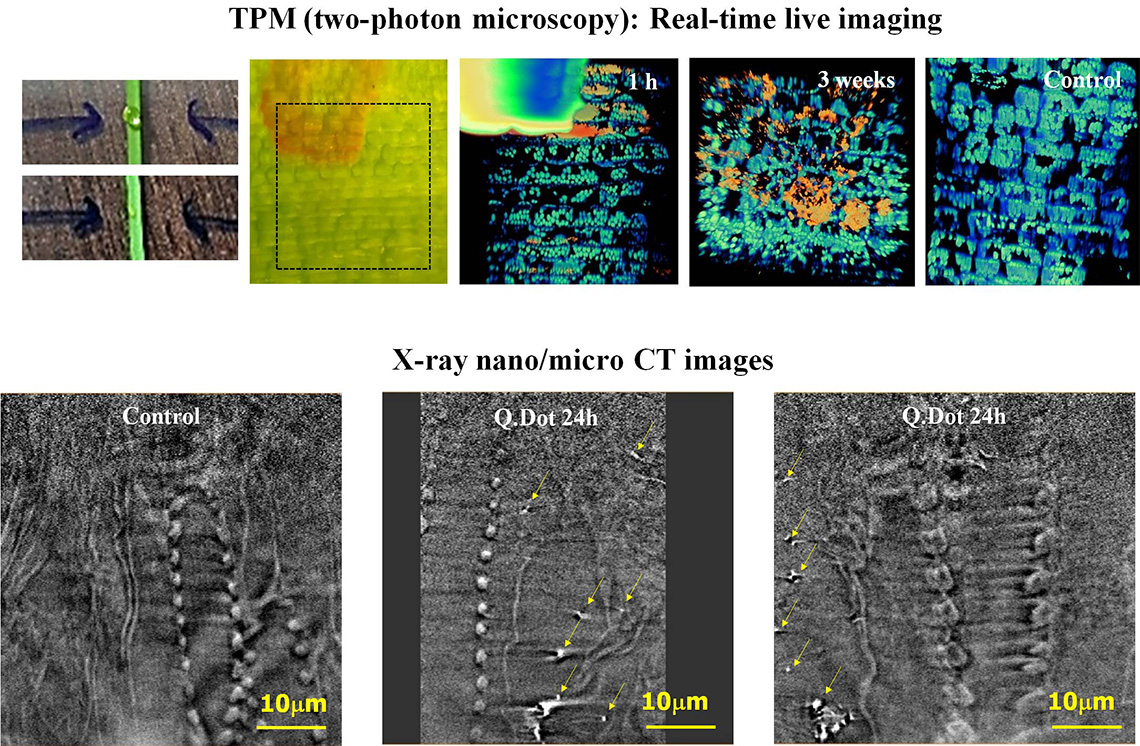
Plant Hydrodynamics and Biomimetics
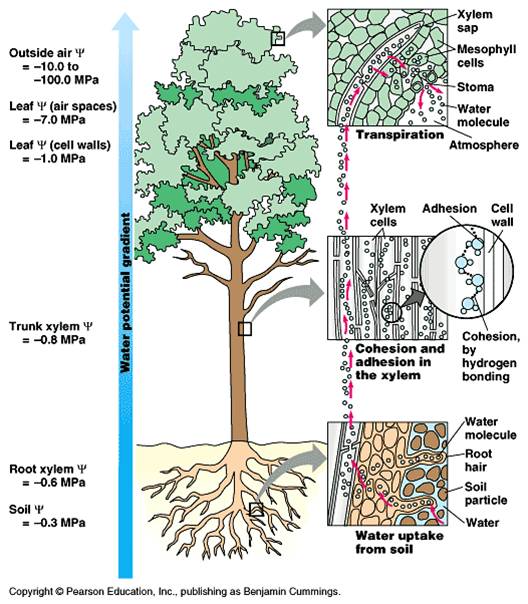
Embolism and water refilling in xylem vessels and embolism repair
Xylem sap transport under negative pressure
Embolism repair and active flow regulation
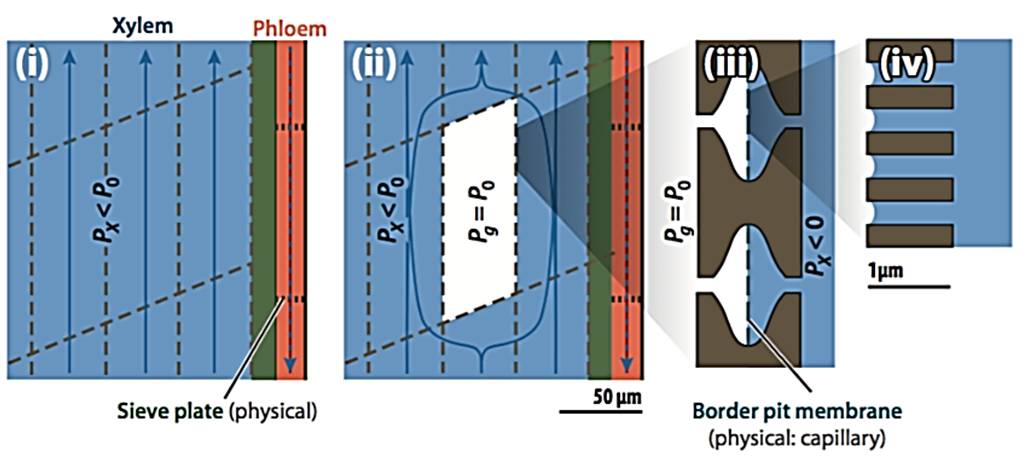
Stop-and-acceleration pattern in the xylem-inspired channel
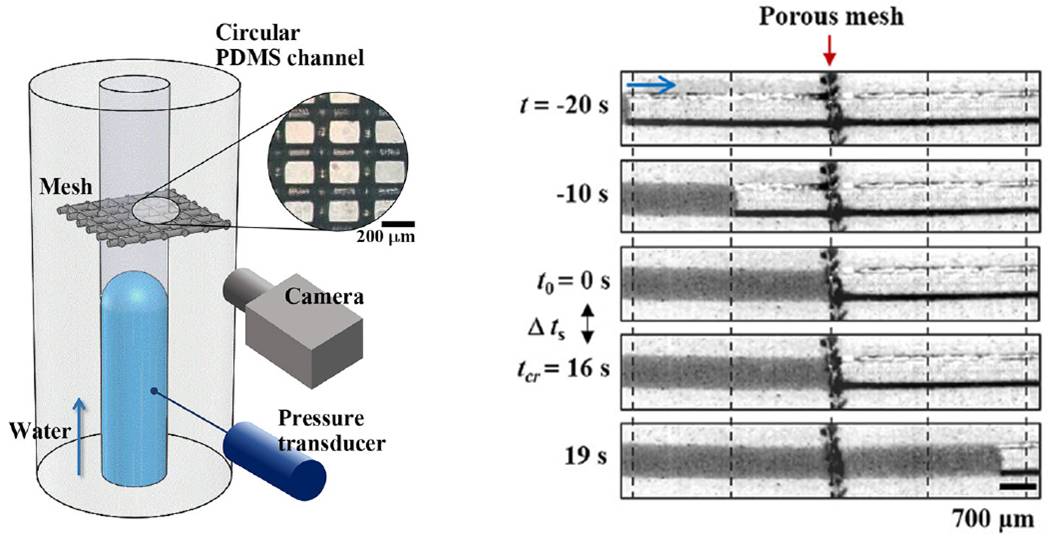
Three-steps of water-filling process at porous mesh
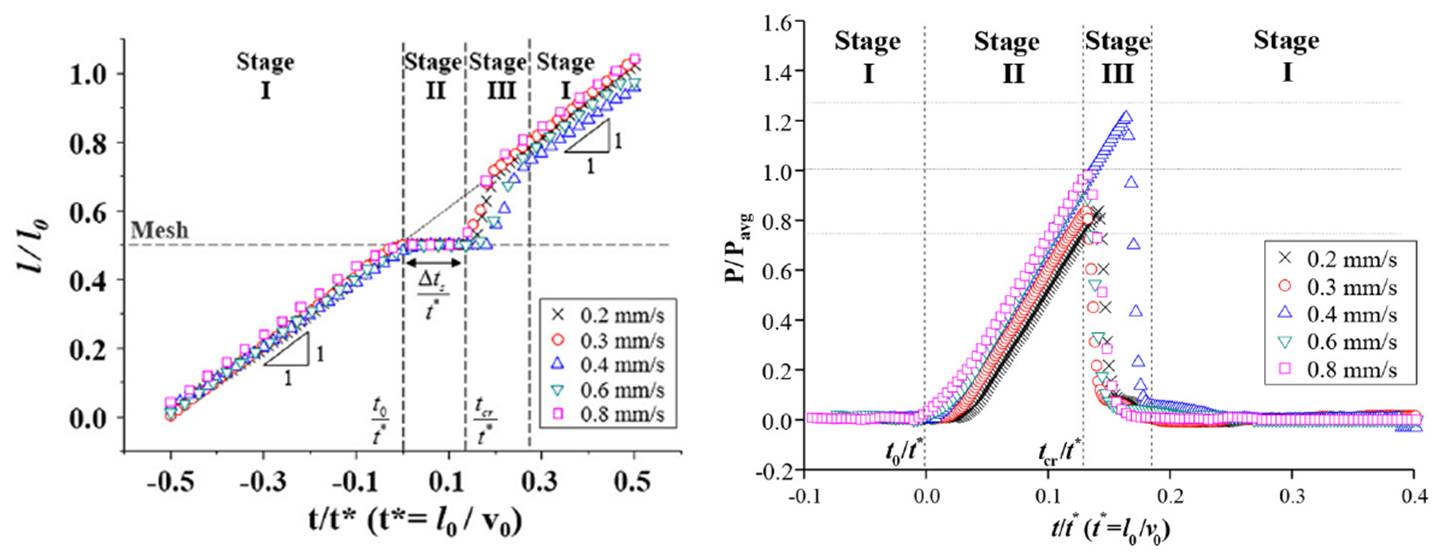
Stop-and-acceleration flow phenomena
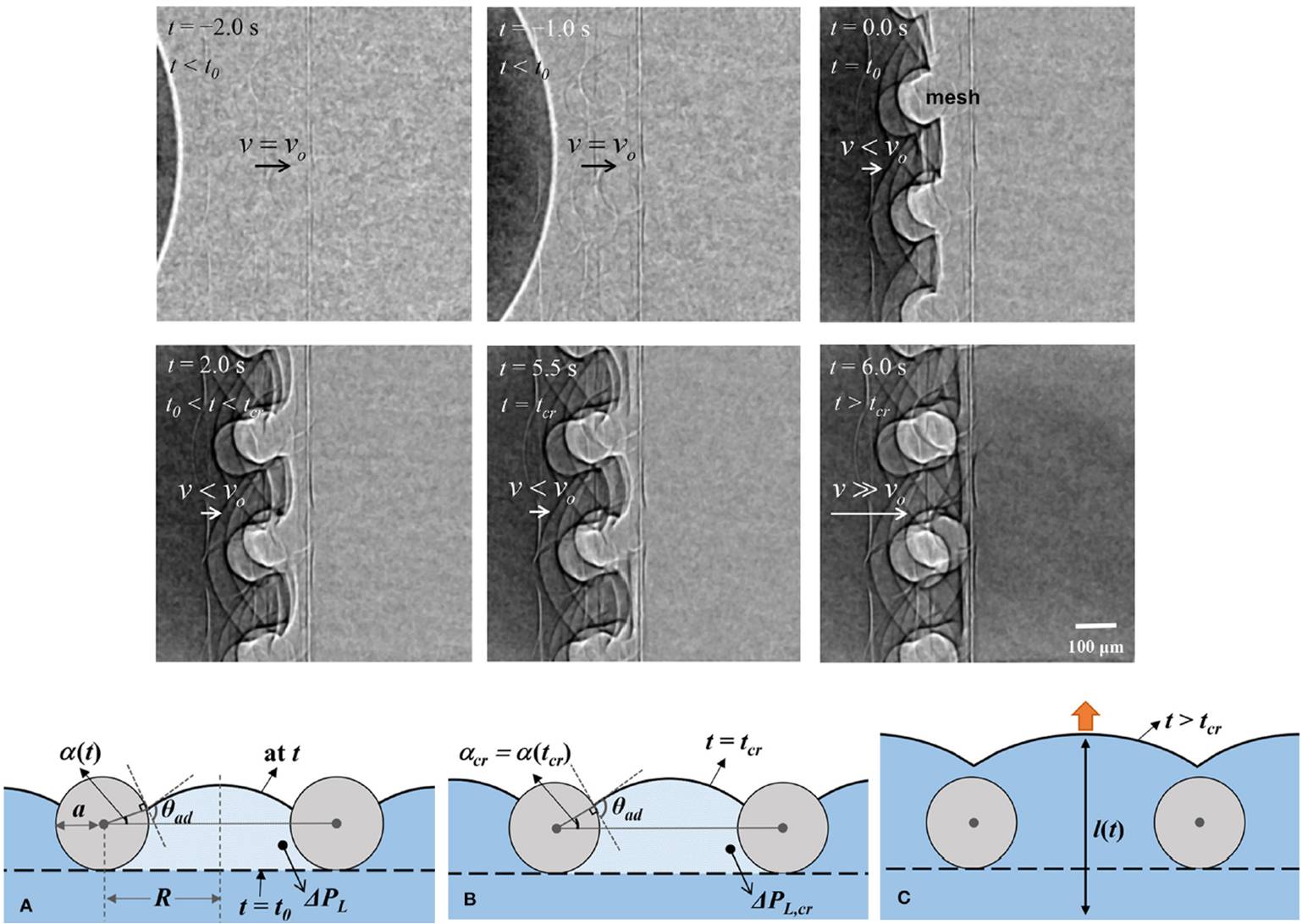
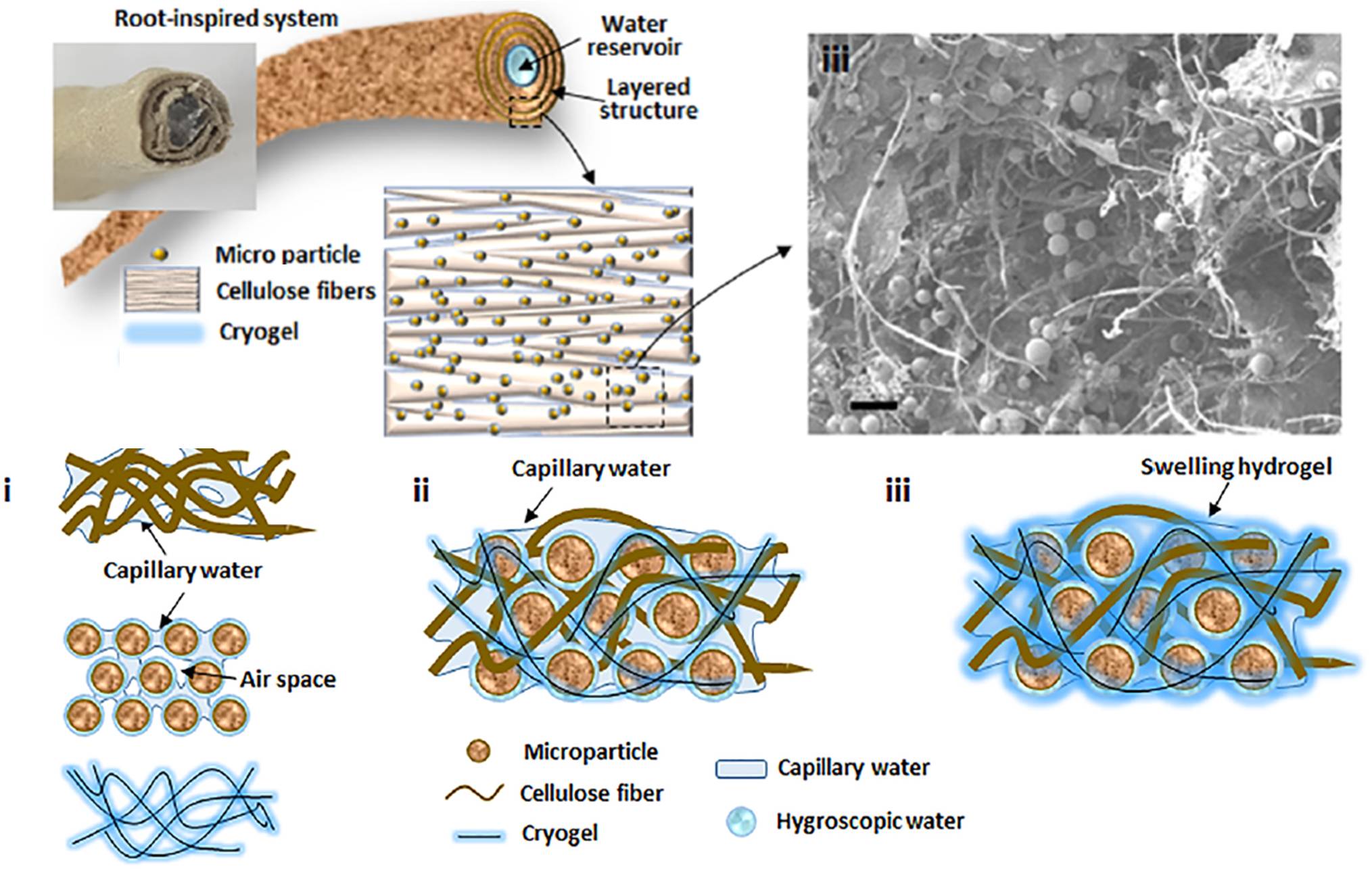
Water absorption inspired by cactus root
Structural and functional features of cactus root
Water management abilities of CRIM
Schematic diagram of cactus root-inspired model (CRIM)
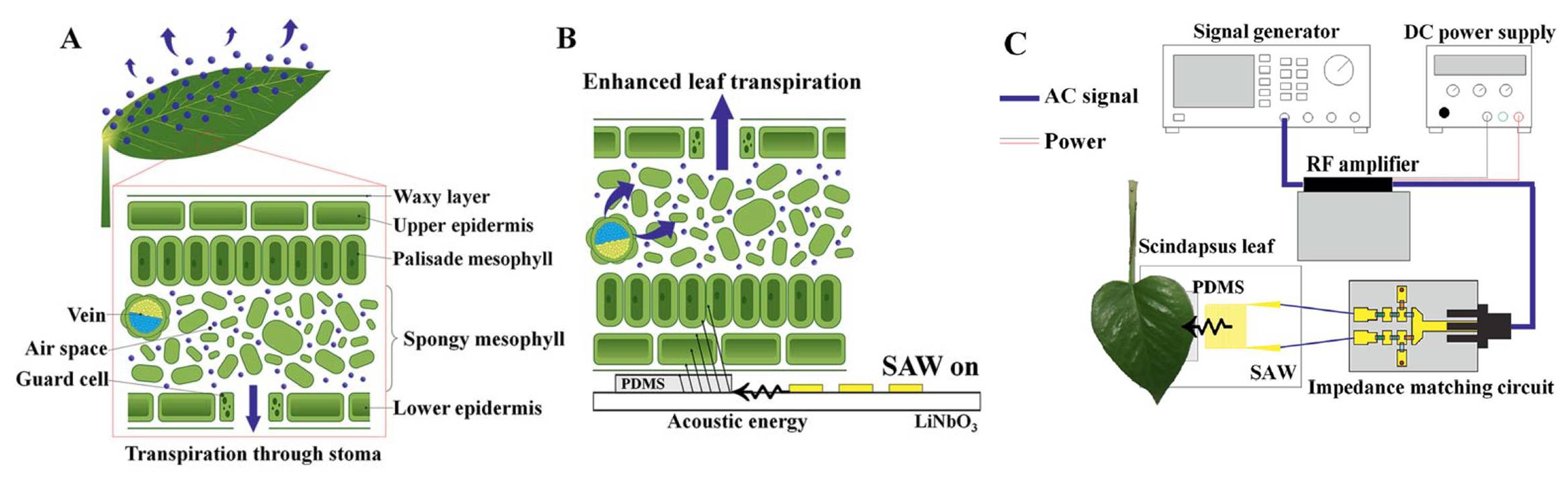
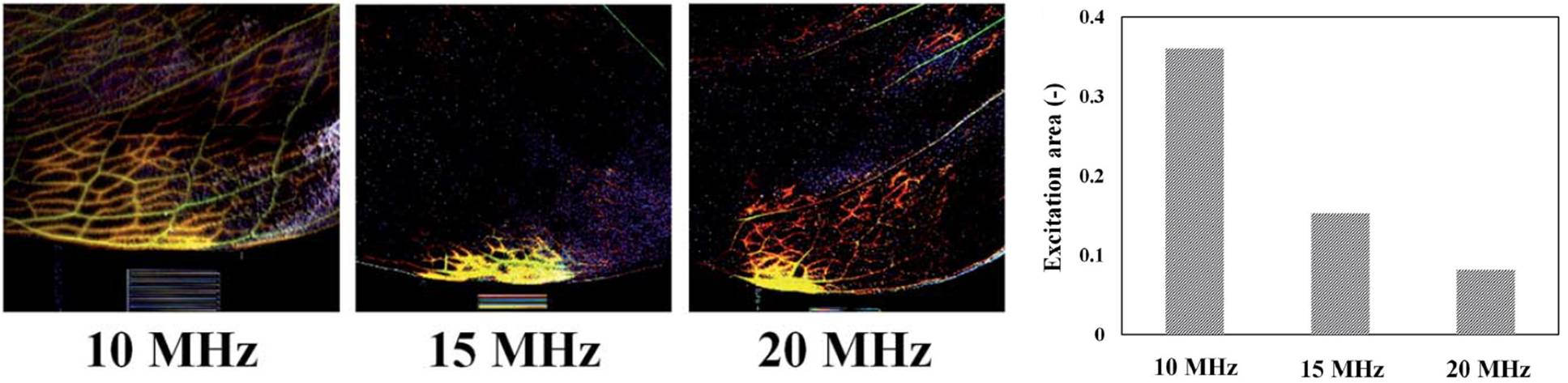
Enhancement of leaf transpiration by surface acoustic wave (SAW)
Internal structures of a plant leaf and SAW activation
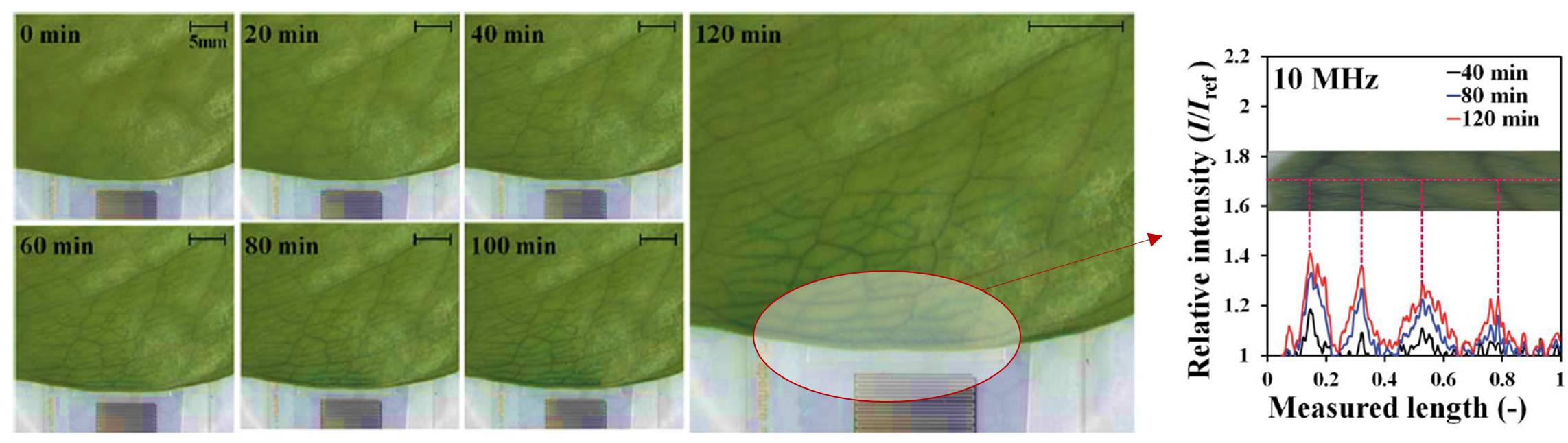
Sequential images showing local delivery of dye solution in plant leaf
Leaf transpiration activated by SAW frequencies
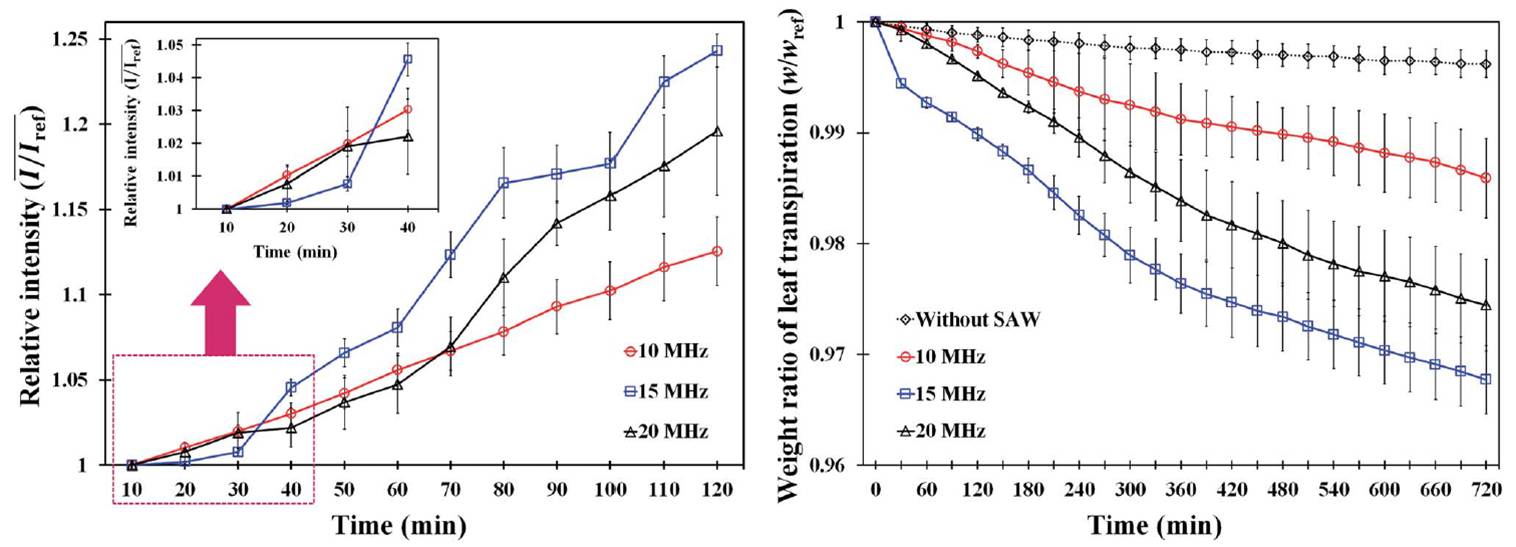
Measurement of the excitation lengths and areas
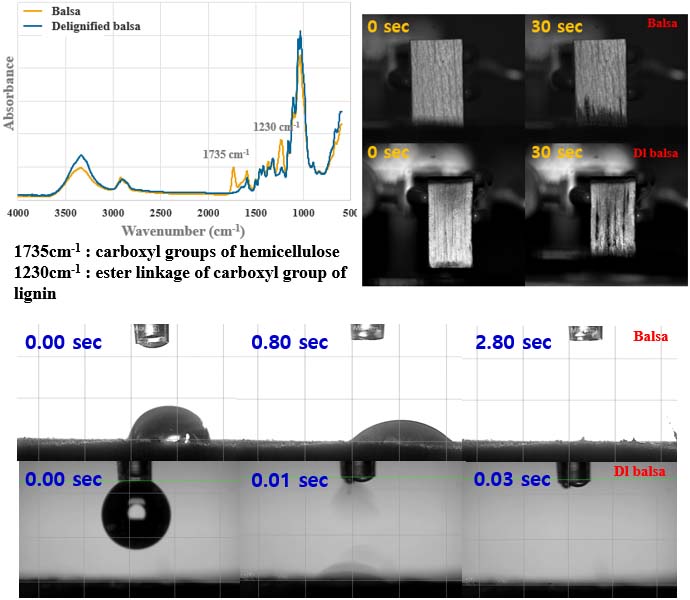
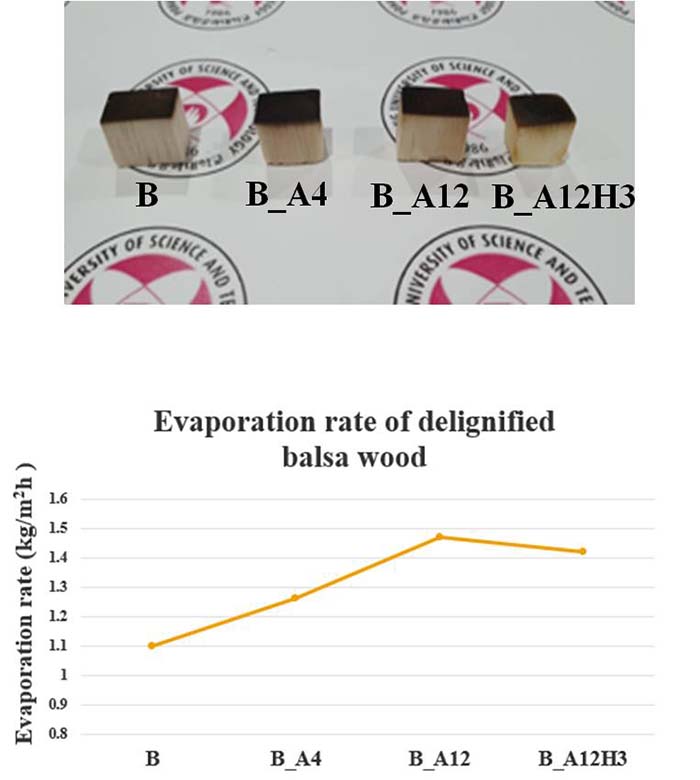
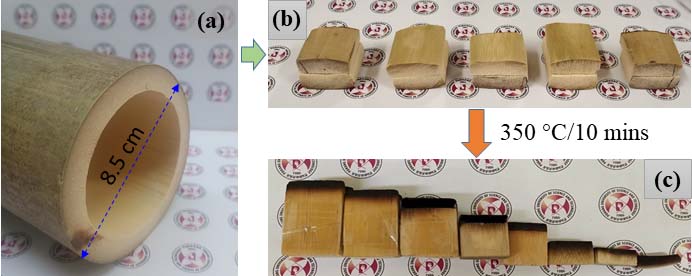
Wood-based solar-driven desalination
Waste biomass-based solar absorber for solar-driven desalination and water treatment
Bamboo-based solar absorber for seawater desalination
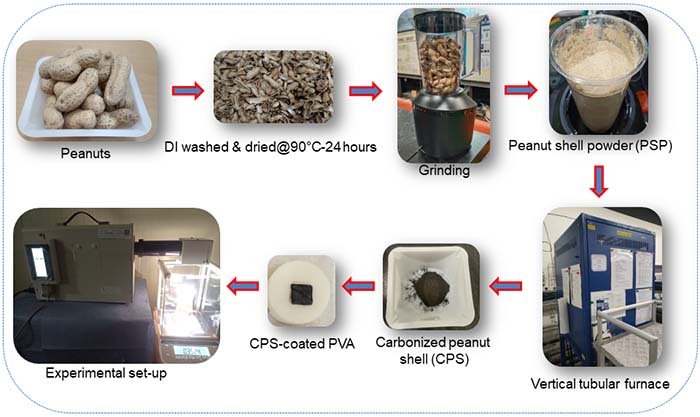
Peanut shell-derived photothermal absorber for solar desalination

Hydrogel & aerogel based interfacial solar steam generation (ISSG) for desalination
Functionalization of porous polymer network
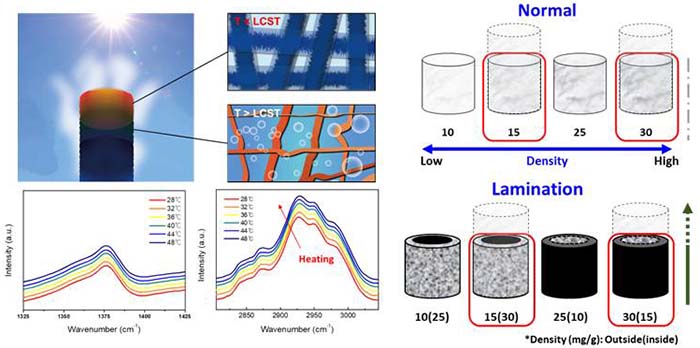
- Functionalized polymers are utilized for ISSG
- Thermo-responsive properties, bilayered lamination, or ionic polymeric constituents are utilized
Three-dimensional ISSG structures
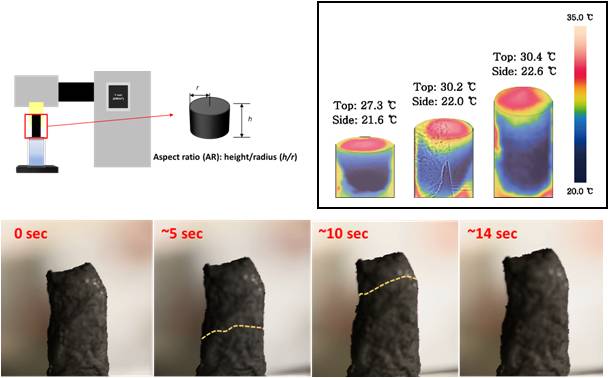
- Evaporation behaviors are studied with changing aspect ratio, porosity, thermal properties of solar absorbers
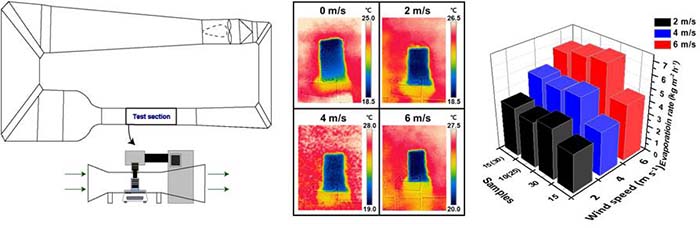
3D ISSG evaporators with convective flow
Anti-salt property of solar absorbers
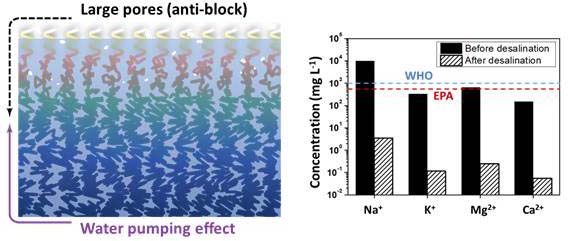
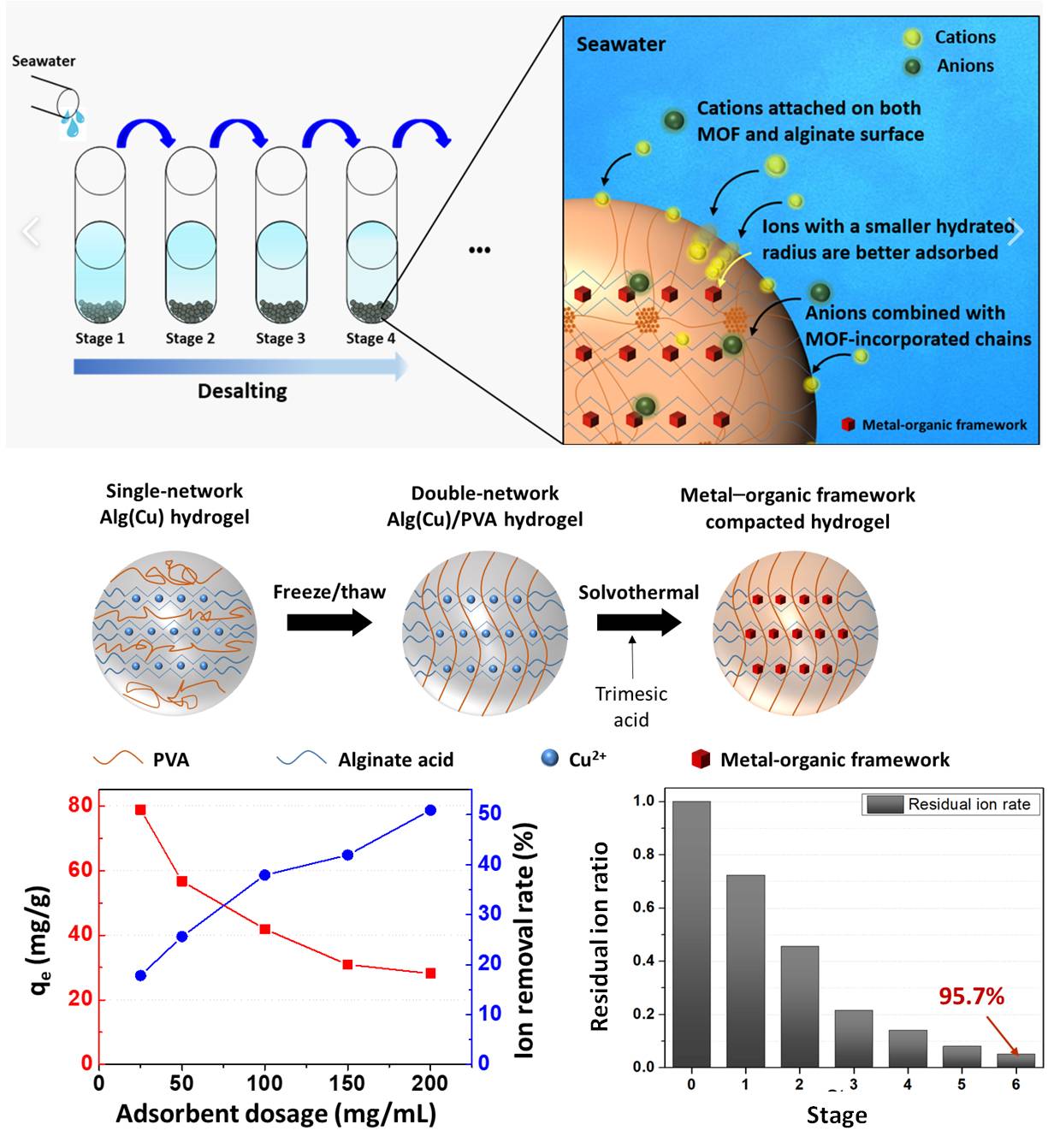
Seawater Desalination Ion-adsorptive MOF adsorbents of seawater to reduce salt concentration
MOF-incorporated alginate/PVA adsorbent
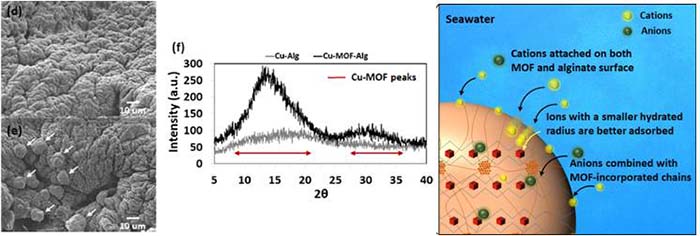
- Metal-organic framework (MOF) is utilized to capture salt ions from seawater to decrease salinity
- Alginate/PVA based double networks stably adsorb salts
Three-dimensional ISSG structures
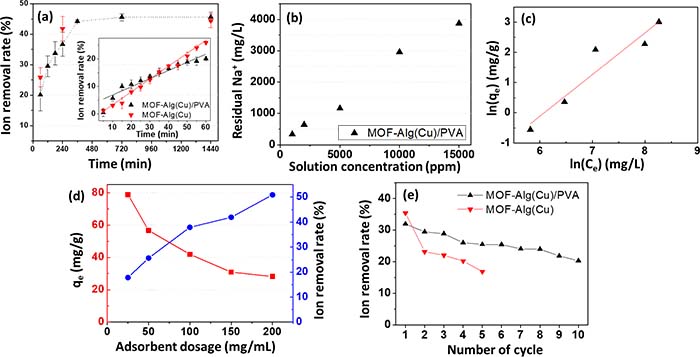
- Many parameters are investigated to enhance ion removal rate and stability of desalination system
3Hybrid seawater desalination experiment
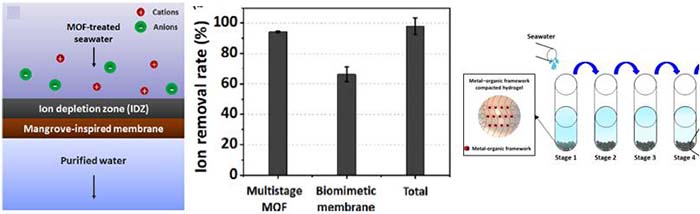
- Beads-type adsorbents can be applied into another desalination techniques, such as membrane filtration, etc.
특허 정보 등록번호: 1023324340000 / 출원번호: 1020200127214
Porous carbon-based 3D steam generator for photothermal-based solar desalination
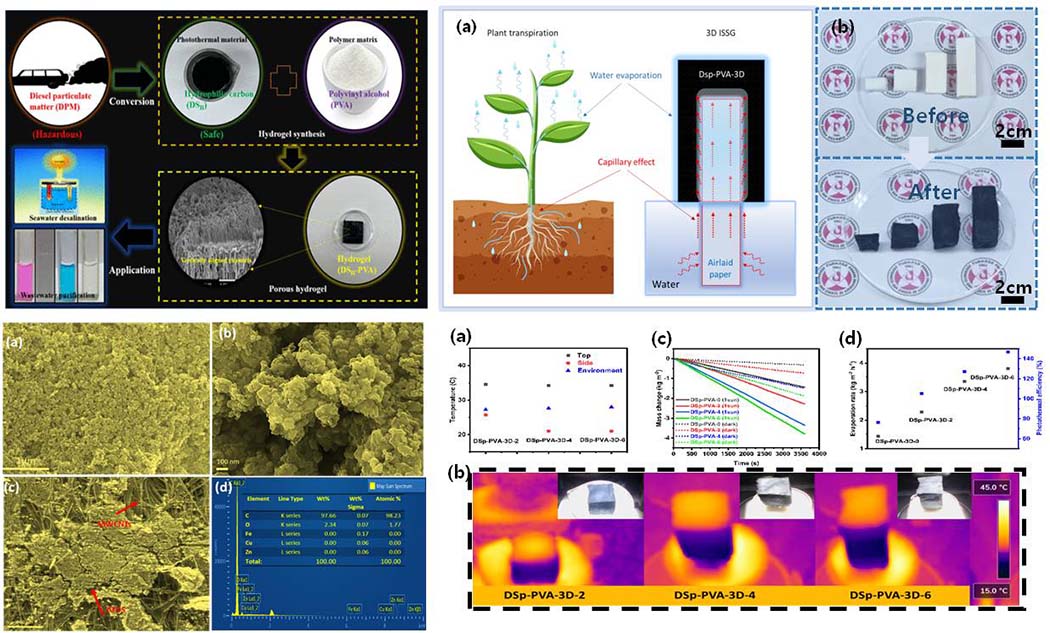
This kind of research offers a promising pathway, integration of solar energy and innovative materials to resolve global water scarcity.